China debt: how big is it now?
- China’s overall debt was 270.1 per cent of gross domestic product at the end of 2020, up from 246.5 per cent at the end of 2019
- China’s outstanding foreign debt, including US dollar debt, reached US$2.4 trillion in 2020
What is the nature of China’s debt?
Broadly speaking, China’s debt can be divided into domestic debt and foreign debt.
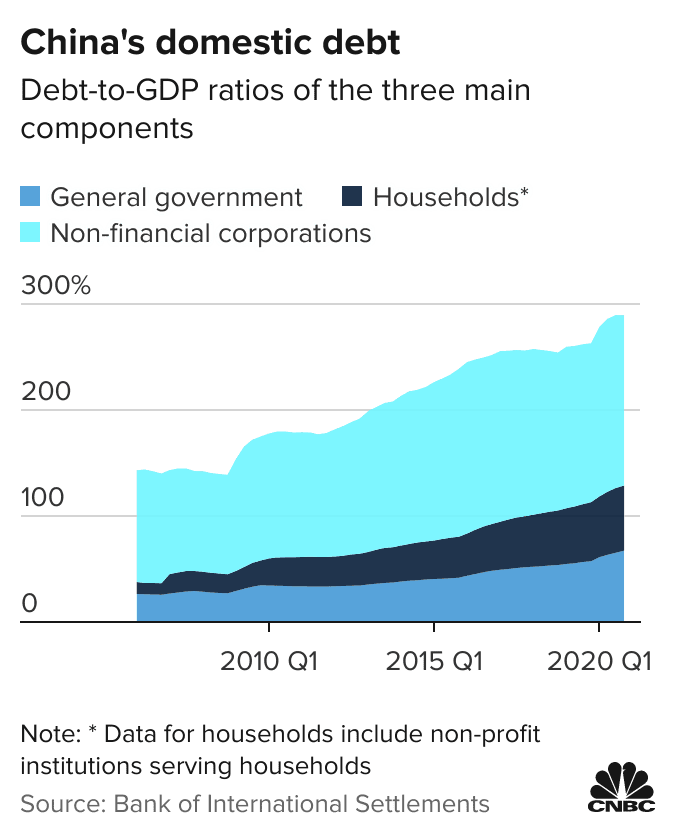 China’s
domestic debt, denominated in yuan, consists of three components:
corporate, household and government debt. Corporate debt includes
borrowings by private sector and state-owned companies. Public debt is a
combination of national and local government debt.
China’s
domestic debt, denominated in yuan, consists of three components:
corporate, household and government debt. Corporate debt includes
borrowings by private sector and state-owned companies. Public debt is a
combination of national and local government debt.
Household debt is the combined debt of all people in a household, including consumer debt and mortgage loans.
China's external debt
| Year | US$ |
|---|---|
| 1985 | 15.83 billion |
| 1990 | 52.55 billion |
| 1995 | 106.59 billion |
| 2000 | 145.73 billion |
| 2005 | 296.55 billion |
| 2010 | 548.94 billion |
| 2015 | 1.38 trillion |
| 2020 | 2.4 trillion |
Source: China’s State Administration of Foreign Exchange
China’s foreign debt in currencies other than the yuan includes private sector firms’ borrowing from foreign banks, trade-related credit to Chinese firms from foreign trading partners, and debt securities issued by Chinese state-owned and private sector firms to foreign investors.
What about debt that the world owes China?
Almost all of this lending is official, coming from the government and state-controlled companies. Over the years, China has been lending to emerging economies such as those in Africa.
China is also a large holder of US Treasuries, effectively funding federal budget deficits in the United States. However, many of the borrowings in developing countries are between governments, and China often does not disclose details or terms of the loans.
China has also been expanding its overseas projects financed by state-backed loans under the Belt and Road Initiative, an ambitious infrastructure investment plan to build rail, road, sea and other routes stretching from China to Asia, Africa and Europe.
According to a report by the Institute of International Finance in January 2021, China’s outstanding debt claims on the rest of the world increased from about US$1.6 trillion in 2006 to more than US$5.6 trillion as of mid-2020, making China one of the biggest creditors to low-income countries.
What is China’s current debt level?
 China’s
debt levels rose significantly in 2020 as a result of looser fiscal
policy to help revive the coronavirus-hit economy. But the Chinese
government has since said debt reduction is now a priority in preventing
more bad debt from building up.
China’s
debt levels rose significantly in 2020 as a result of looser fiscal
policy to help revive the coronavirus-hit economy. But the Chinese
government has since said debt reduction is now a priority in preventing
more bad debt from building up.
China’s National Institution for Finance and Development (NFID), a government-linked think tank, put the nation’s overall debt at 270.1 per cent of gross domestic product (GDP) at the end of 2020, up from 246.5 per cent at the end of 2019.
Overall leverage declined by 2.1 percentage points in the first quarter of 2021 to 268 per cent of GDP.
Household debt to GDP declined for the first time on a quarterly basis since 2012, but only by a small fraction, according to NFID, from 62.2 per cent at the end of 2020 to 62.1 per cent in the first quarter of 2021. Within the household debt category, consumer loans rose from 13.4 per cent in late 2020 to 13.9 per cent in the first quarter of 2021.
Public debt to GDP fell the most out of all the categories in the first quarter of 2021. The NFID’s estimates showed that the leverage ratio of local governments fell from 25.6 per cent at the end of 2020 to 24.7 per cent in the first quarter of 2021.
China’s outstanding foreign debt, including US dollar debt, reached US$2.4 trillion at the end of 2020, up 4 per cent compared with the total at the end of September 2020, according to China’s State Administration of Foreign Exchange.
Who owns China’s debt?
Most of China’s local government debt is held by state-owned or state-controlled financial institutions. For decades, China’s local governments have relied on off-balance-sheet borrowing through local government financing vehicles (LGFVs).
Many of these borrowings are not recorded, and transparency is weak when it comes to how the funds are used. Such hidden debts were estimated to be between 30 trillion yuan (US$4.2 trillion) and 40 trillion yuan by Standard & Poor’s in 2018.
By comparison, outstanding local government debt totalled 26.6 trillion yuan at the end of April, according to the Ministry of Finance.
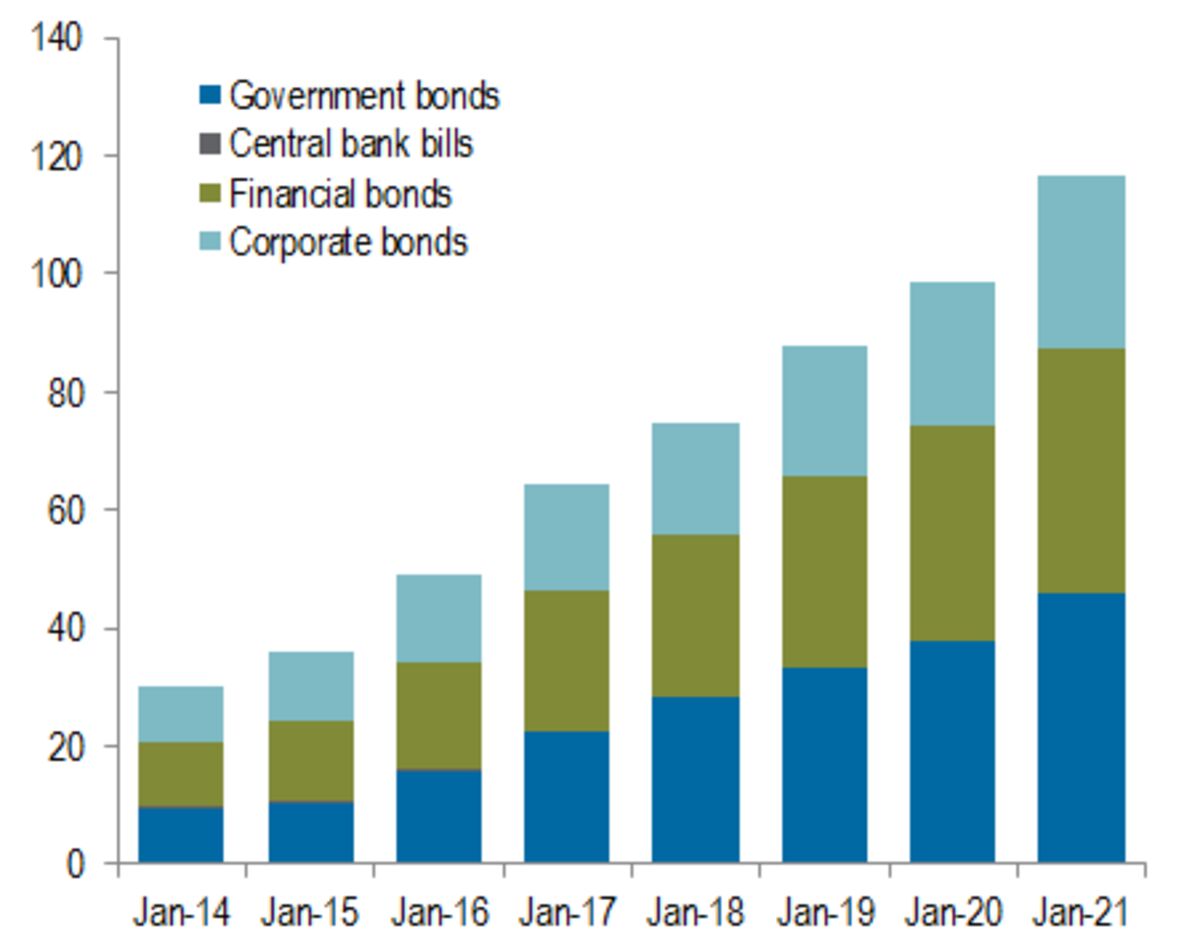
Chinese debt is typically held by domestic institutional investors such as commercial banks, followed by policy banks, which are state-owned banks whose investment and lending practices support government policies, including issuing bonds to raise funds for infrastructure investment and insurance companies.
Foreign investors, on the other hand, have been putting their money in China’s bond market, which consists of bonds issued by the national government, local governments and private companies, along with mortgage-backed securities and other asset-backed securities.
The Chinese bond market is now the second-largest behind that of the US. Since 2016, it has become accessible to foreign investors through government-controlled schemes such as the Bond Connect programme and the Qualified Foreign Institutional Investor scheme.
Foreign investors, including wealth managers, mutual funds, family offices and hedge funds, held 3.62 trillion yuan worth of Chinese bonds at the end of April, making up around 3.4 per cent of all bonds traded in the interbank market.
A total of 58 per cent of these bonds are Treasury bonds, and 27.9 per cent are invested in policy bank bonds, according to data from the People’s Bank of China.
How has China’s debt level changed?
China’s domestic debt has been growing at an average annual rate of around 20 per cent since 2008, faster than its GDP growth. In a bid to counter the impact of the global financial crisis, Beijing unleashed a 4 trillion yuan (US$586 billion) stimulus package in 2008 to boost its economy, which led to a surge in borrowing by local governments and state-owned firms.
But since 2016, China has increased efforts to reduce its debt pile to curb financial risks under a deleveraging campaign led by the central bank. The pandemic that began in 2020, however, has sent China’s overall leverage ratio up again.
As a result, the Chinese government has renewed its efforts to control domestic debt levels, especially in the speculative property market. A series of defaults in bonds sold by state firms controlled by local governments late in 2020 also raised fears that it could trigger a financial crisis in China’s state-dominated banking sector.
In April, the State Council, the government’s cabinet, said that LGFVs, which are used by local governments to sidestep borrowing limits, should restructure or go bankrupt if they are unable to pay back debt.
After years of rapid growth, China’s external debt has also grown, partly because of the country’s push to acquire foreign assets.
Its overseas expansion, though, has slowed somewhat since 2015 because of a combination of factors such as sluggish domestic growth, capital and regulatory controls and increasing scrutiny by foreign countries of Chinese investment.




No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.